Hi Guys, In this post I'll share some Basic Variable Concepts in Java which will very help full for beginners.
Guys be ready to implement those concepts in your system after getting boost up .
What's a variable Gys?
In a discussion friends i found, A variable can be thought of as a container which holds value for you, during the life of a Java program. Every variable is assigned a data type which designates the type and quantity of value it can hold.
In order to use a variable in a program you to need to perform 2 steps -
Guys be ready to implement those concepts in your system after getting boost up .
What's a variable Gys?
In a discussion friends i found, A variable can be thought of as a container which holds value for you, during the life of a Java program. Every variable is assigned a data type which designates the type and quantity of value it can hold.
In order to use a variable in a program you to need to perform 2 steps -
- Variable Declaration- To declare a variable, you must specify the data type & give the variable a unique name.
Examples of other Valid Declarations are
int a,b,c;
float pi;
double d;
char a;
- Variable Initialization- To initialize a variable, you must assign it a valid value.
Example of other Valid Initializations are
Example-
int a=2,b=4,c=6;
float pi=3.14f;
double do=20.22d;
char a=’v’;
Types Of variable in Java- There are three types of variable in java.
1). Local variable- Local Variables are a variable that are declared inside the body of a method.
2). Instance Variable- Instance variables are defined without the STATIC keyword .They are defined Outside a method declaration. They are Object specific and are known as instance variables.
3). Static Variable- Static variables are initialized only once, at the start of the program execution. These variables should be initialized first, before the initialization of any instance variables.
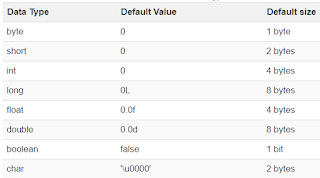
Data Types in Java- Data types classify the different values to be stored in the variable. In java, there are two types of data types:
1). Primitive Data Types
2). Non-primitive Data Types
Primitive Data Types are predefined and available within the Java language. Primitive values do not share state with other primitive values.
There are 8 primitive types: byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, and boolean Integer data types
byte (1 byte)
short (2 bytes)
int (4 bytes)
long (8 bytes)
Floating Data Type-
float (4 bytes) double (8 bytes)
Textual Data Type-
char (2 bytes)
Logical-
boolean (1 byte) (true/false
Java Data Types-
Java Variable Type Conversion & Type Casting
A variable of one type can receive the value of another type. Here there are 2 cases -
Java Variable Type Conversion & Type Casting
A variable of one type can receive the value of another type. Here there are 2 cases -
Case 1). Variable of smaller capacity is be assigned to another variable of bigger capacity.
This process is Automatic, and non-explicit is known as Conversion
Case 2)- Variable of larger capacity is be assigned to another variable of smaller capacity
In such cases, you have to explicitly specify the type cast operator. This process is known as Type Casting.
In case, you do not specify a type cast operator; the compiler gives an error. Since this rule is enforced by the compiler, it makes the programmer aware that the conversion he is about to do may cause some loss in data and prevents accidental losses.
Cheers Friends :)








No comments:
Post a Comment